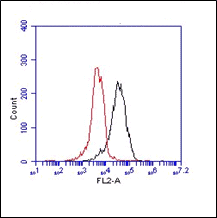
SAP, Mouse, pAb
€139.00 €431.00Price range: €139.00 through €431.00
The polyclonal antibody recognizes serum amyloid P (SAP). Serum amyloid P component (SAP) belongs to a highly conserved superfamily of calcium-dependent ligand binding and lectin (carbohydrate binding) proteins. Due to the pentameric structure these proteins are also called pentraxins. SAP is 25kDa in size. C-reactive protein (CRP) and SAP are well-charactarized short pentraxins, which are produced in the liver in response to inflammatory mediators. Pentraxin 3 (PTX3) is the prototypic long pentraxin. Both SAP and CRP are evolutionary conserved in all vertebrates and found in distant invertebrates such as the horseshoe crab (Limulus polyphemus). They share 51% residue sequence identity and 66% homology.
SAP is highly resistant to proteolysis, especially when it forms complexes with calcium-dependent ligands. SAP avidly binds to macromolecular ligands, such as nucleosomal DNA, glycosaminoglycans and amyloid fibrils. When aggregated it can bind C1q and activate the classical complement pathway.
Human SAP is not an acute phase reactant following acute stimuli, this in contrast to mouse SAP and human CRP. In mouse, SAP levels increase significantly 24 hours after challenge with lipopolysaccharide.
SAP is a normal plasma constituent that is present in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), in the pathognomonic lesions of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), cerebrovascular and intracerebral Aβ amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. This is a result of its binding to amyloid fibrils and to paired helical filaments, respectively. The protein itself may also be directly neurocytotoxic. SAP contributes significantly to the pathogenesis of amyloidosis. The mechanism of its participation is not yet known and importantly may differ between species.