NOD2, Human, mAb hNOD2.017
€133.00 – €414.00
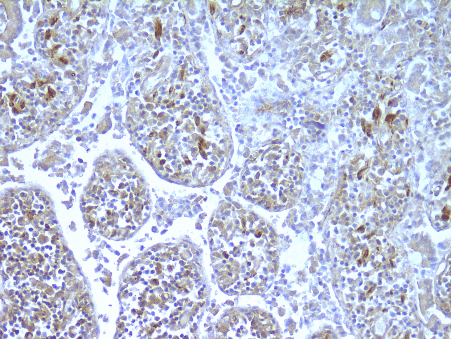
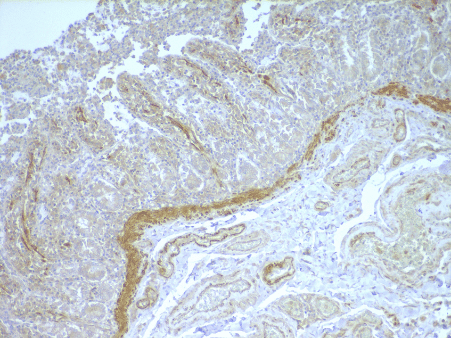
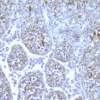
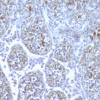
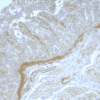
Monoclonal antibody 2.017 recognizes human NOD2, also known as CARD15. The innate immune system is the first line of defense against pathogens using various pattern recognition receptors (PRR). PRRs include toll-like receptors (TLRs), nucleotide-biding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptors (NLRs) and retinoic acid-inducible (RIG)-I-like receptors (RLR). The Nod-like receptor (NLR) family of proteins consists of cytosolic pattern recognition molecules involved in sensing microbial and danger signals and triggering innate immune activation. The NOD family is involved in the regulation of apoptosis and the immune response. The founding members of NLRs are NOD1 and NOD2. These intracellular receptors recognize peptidoglycans. The receptor consists of three main domains. The C-terminal site recognizes the ligand via the leucin-rich repeat domain (LRR). The NOD domain facilitates the self-oligomerization and contains the ATPase activity. The N-terminal site is the caspase-recruitment domain (CARD). Proteoglycans are polymers composed of glycan chains of alternating N-acylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) units cross-linked to each other by short peptides. The cross-linking of two parallel glycan chains is mediated by stem peptides that can be further linked by bridging amino acids. For activation of the immune system, NOD2 senses muramyl dipeptide (MDP), which is found in the PGN of nearly all Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms, whereas NOD1 recognizes meso-diaminopimelic acid (meso-DAP)-containing PGN fragments. Stimulation of NOD1 or NOD2 results in the activation of NF-κB and MAPKs, through a homophilic interaction with the adaptor kinase, Rip2. Thereby driving the transcription of numerous genes involved in both innate and adaptive immune responses. NOD2 seems of special importance in commensal homeostasis and especially in the gut. This is reflected by the fact that genetic variation has been found in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), particularly Crohn’s disease. NOD2 is mainly expressed by macrophages, monocytes as well as Paneth cells, T and B cell, dendritic cells and intestinal epithelial cells. NOD2 antibody 2.017 can be used for western blotting, immunohistochemistry, ELISA and immunoprecipitation.