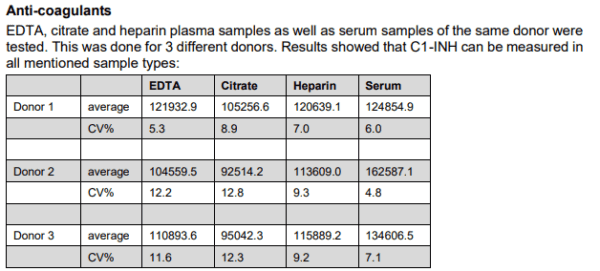
C1-INH, Human, ELISA
C1 Inhibitor (C1-INH), a central regulator of the complement system, plays a pivotal role in modulating immune response, with critical implications in both innate and adaptive immunity.
Read more€756.00 €1,223.00Price range: €756.00 through €1,223.00
C1 Inhibitor (C1-INH) stands as a sentinel in immune regulation, orchestrating the delicate balance of our body’s defense mechanisms. As a master suppressor, C1-INH targets key enzymes across various immune pathways, safeguarding against unwarranted inflammation and preserving vascular stability. Its distinctive function in conserving the Alternative Pathway, while meticulously regulating the Classical and Lectin pathways, marks it as an integral component in immune homeostasis. In the clinical realm, C1-INH is pivotal in managing hereditary angioedema (HAE)—a condition marked by sudden, intense swelling. As a diagnostic marker, C1-INH is gaining recognition for its potential to detect early signs of MIS-C, SLE, and MS, heralding a new era in the proactive management of these complex conditions.
The efficient format of a plate with twelve disposable 8-well strips allows free choice of batch size for the assay.
Samples and standards are incubated in microtiter wells coated with antibodies recognizing Human C1-INH.
Peroxidase-conjugated antibody will bind to the captured C1-INH.
Peroxidase-conjugate will react with the substrate, tetramethylbenzidine (TMB).
The enzyme reaction is stopped by the addition of oxalic acid.
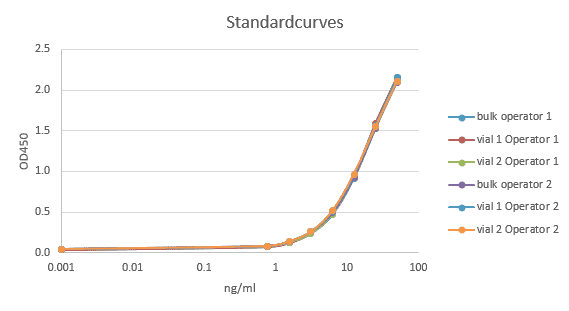
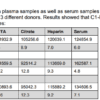
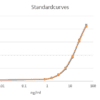
The absorbance at 450 nm is measured with a spectrophotometer. A standard curve is obtained by plotting the absorbance (linear) versus the corresponding concentrations of the Human C1-INH standards (log).
The Human C1-INH concentration of samples, which are run concurrently with the standards, can be determined from the standard curve.
You may be interested in…
-
View product €825.00 €1,359.00Price range: €825.00 through €1,359.00
-
View product €894.00 €1,443.00Price range: €894.00 through €1,443.00
-
View product €756.00 €1,223.00Price range: €756.00 through €1,223.00