C5/C5a, Human, mAb 557
€133.00 – €414.00
Monoclonal antibody 557 specifically recognizes an epitope of complement factor 5 (C5) and its active fragment, C5a. The complement system, comprising over 30 proteins, is activated in response to tissue injury, invading pathogens, or foreign surfaces. It plays a critical role in both the activation and lytic pathways of the immune response.
In the complement activation pathways, C5 is cleaved after C3, producing C5a—a well-characterized cleavage product with potent chemotactic and anaphylatoxic properties. C5a is essential for the innate immune response and is increasingly recognized for its role in adaptive immunity as well. C5a is a 74-residue pro-inflammatory polypeptide that triggers various immune functions, including smooth muscle contraction, increased vascular permeability, and the release of lysosomal enzymes. It also promotes the directed migration of neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes.
C5a exerts its effects primarily through two receptors: C5aR (also known as C5R1 or CD88) and C5L2 (gpr77). These seven-transmembrane domain receptors are widely expressed, especially on immune cells such as macrophages, neutrophils, and T cells. C5aR is well-known for initiating G-protein-coupled signaling pathways that stimulate the production of cytokines like TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, IL-6, and IL-8. Blocking C5aR has been shown to significantly reduce inflammatory damage in vivo. In contrast, the function of C5L2 is less understood, as its interaction with C5a does not trigger calcium signaling.
The widespread presence of C5a receptors throughout the body allows C5a to mediate a broad range of effects. Consequently, C5a is a key pathogenic factor in various immuno-inflammatory diseases and has been implicated in non-immunological processes like CNS development, neurodegeneration, tissue regeneration, and hematopoiesis.
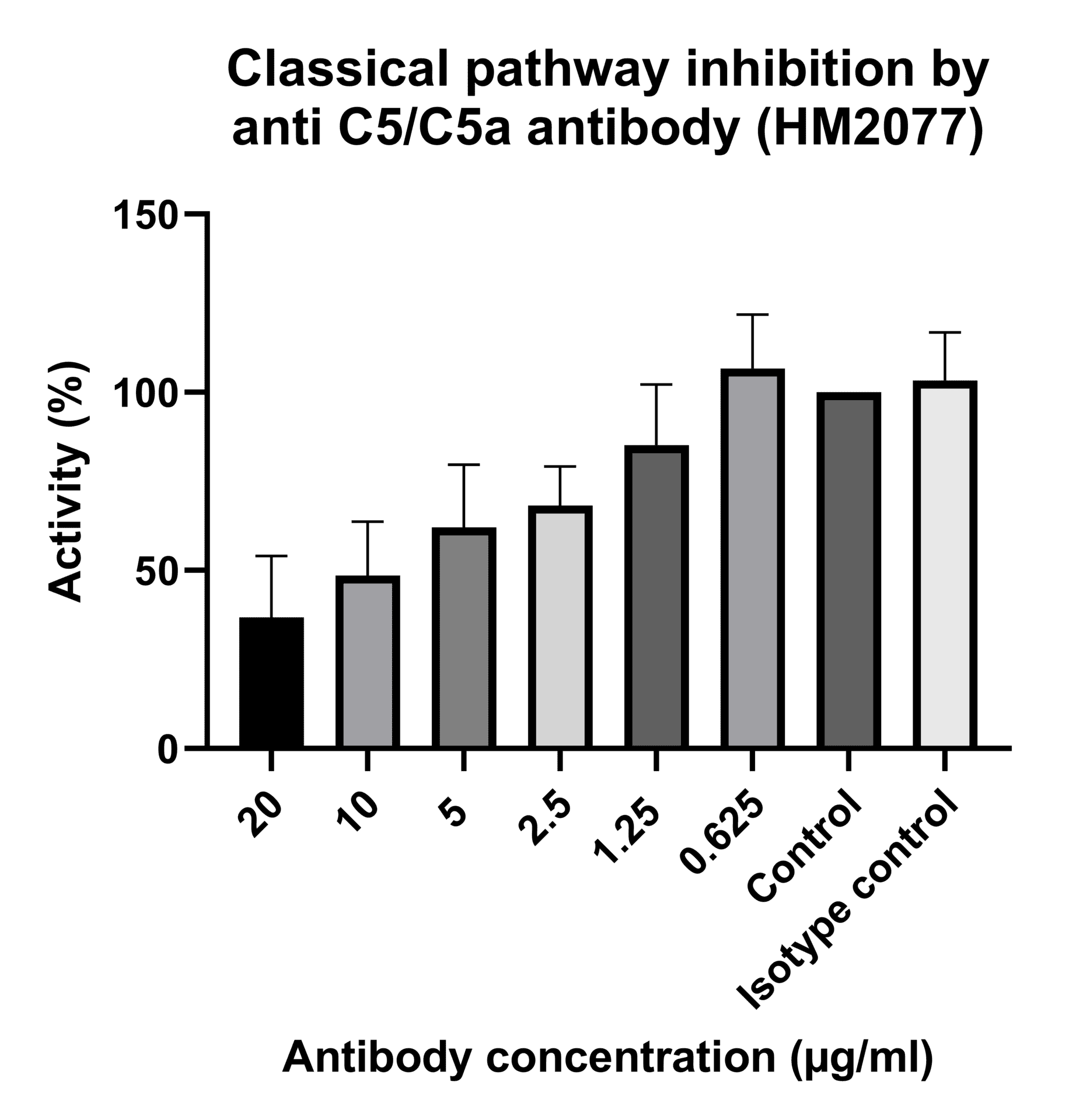
Monoclonal antibody 557 effectively inhibits the binding of C5a to the C5a receptor through a competitive mechanism, preventing receptor activation. However, it does not interfere with the cleavage of C5 into C5a and C5b. The inhibition of the classical pathway can be measured with the human classical pathway assay (HK3010).
W: used as ascites at a 1/1000 dilution. Incubation 2h on nitrocellulose blotted samples. (Ref.1)