MASP-2/MAp19, Human, mAb 6G12
€133.00 – €1,245.00
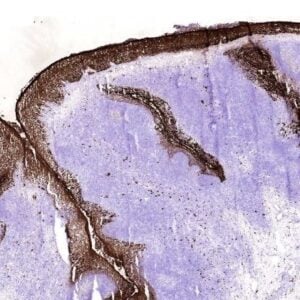
The monoclonal antibody 6G12 reacts with human MASP-2 and human MAp19. MASP-2 is a trypsin-like serine protease and plays an important role in the initiation of the MBL complement activation pathway. Three pathways of complement activation have been reported: the antibody-dependent classical pathway, the antibody-independent alternative pathway and the lectin pathway. Activation of each pathway involves formation of serine protease complexes, which results in activation of the central complement component C3. In the lectin pathway, mannose binding-lectin (MBL)-associated serine proteases (MASPs) form complexes with polymeric lectin molecules which are involved in pattern recognition. Upon binding of the recognition molecules to carbohydrates on the surface of micro organisms, MASPs are converted to their active forms and initiate complement activation. Three types of human MASP have been reported. MASP-1, MASP-2 and MASP-3. Mannan-binding lectin (MBL) and ficolins, in complex with MBL-associated serin proteases (MASPs), are capable of activation the complement system, thus mediating the destruction of infectious agents. MASP-2 cleaves C4 and C2 and is crucial for the activation of downstream complement components. MAp19 is an alternative splicing product of the MASP-2 gene. MAp19 comprises the first two domains of MASP-2 followed by an extra sequence of four unique amino acids (EQSL) at its C-terminal. MASP-2 and MAp19 have been reported to bind to MBL in a calcium-dependent manner.
The monoclonal antibody 6G12 reacts with high affinity to the N-terminal end of MASP-2 and Map19.
W: Both reduced and non-reduced can be performed. The expected band size for MASP-2 is approximately 75 kDa and for Map19 approximately 20 kDa.