IL-13R-alpha-1, Mouse, mAb 1G3
€133.00 €414.00Price range: €133.00 through €414.00
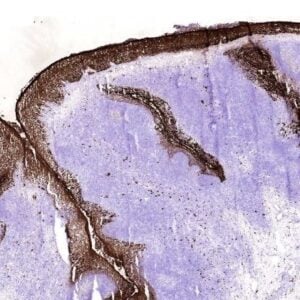
Mouse monoclonal antibody clone 1G3 recognizes mouse Il-13Ralpha1. Il-13 is a cytokine secreted by activated TH2 cells and is important mediator of allergic inflammation. Il-13 signals via interaction with a heterodimeric receptor of Il-4Rα and IL-13Rα. The IL13Rα consist of two cognate receptors, Il13-Rα1 and Il-13Rα2, which are expressed on a wide variety of cells among others B-cells, basophils, eosinophils, and macrophages. IL-13Rα1 is a glycosylated protein of ca 710KD. The receptor itself has a low affinity for IL13. However when paired with Il-4 it has a strong affinity for IL-13. After cytokine binding the receptor signals via JAK/STAT pathway. The heterodimeric receptor signal both with Il-13 and Il-4. Both cytokines have consequently quite comparable function. Il-13Rα2 and the recently discovered soluble Il-13Rα1 are thought to be decoy receptors for Il-13.
Il-13 have been associated with diseases like asthma and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Several studies have indeed shown the regulating role of Il-13 in airway hyper-reactivity leading to e.g. mucus secretion, chemokine production and IgE production. There are also indications that IL-13Rα1 is involved in macrophages differentiation and might serve as a biomarker for the M2 population.
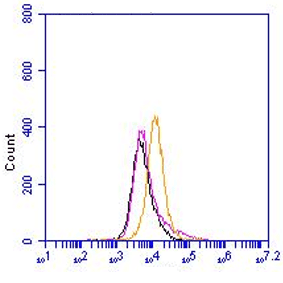
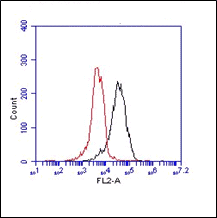
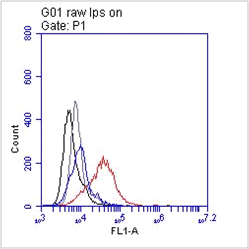
- IP: Intestinal epithelial cells from adult IL-13Rα1-/- and IL-13Rα1+/+ mice were lysed and incubated with purified anti-IL-4Rα (1 μg), anti-IL-13Rα1 (2μg) (1G3), or anti-β actin (0.5 μg) at 4°C overnight (Ref.1).
- W: A reduced sample treatment was used. Expression of IL-13Rα1 in intestinal, lung and liver cells of neonatal and adult IL-13Rα1+/+ BALB/c mice as determined by western blot using an anti-IL-13Rα1 mAb. Intestinal epithelial cells from adult and neonatal IL-13Rα1-/-mice were included as a negative control (Ref.1).