sTCC, sC5b-9 or the membrane attack complex (MAC); its Ambivalent Role: From Immune Defense to Pathological Damage
Basically, the Terminal Complement Complex (TCC) and Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) resemble the same protein complex. The complex can exist as a cell membrane bound variant as well as a soluble variant, respectively referred to as Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) and soluble TCC (sTCC, also called sC5b-9). Multiple studies show changes in sTCC levels during infection, auto-immune diseases and trauma, including traumatic brain injuries. This makes TCC an important marker for complement activation in immunological research.
The complement system has traditionally been associated with natural defense against pathogens. Today we know that the role of complement goes much further than this and makes an important contribution to immune regulation, cellular signaling and disease pathology. The complement cascade is a double-edged sword: beneficial in host defense, but excessive or uncontrolled activation leads to the release of anaphylatoxins, which drive inflammation and can result in tissue damage. Understanding of the regulation of the complement system, and the position of sTCC and MAC within it, is important to gain new insights into its role in both protection and pathology.
We are glad to support you!
Take advantage of our dedicated support team for any technical assistance you need while using our products or considering them for your research needs.
The structural and Functional Definition of sTCC
The soluble Terminal Complement Complex (sTCC), also named sC5b-9, is the soluble form of the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) and represents the end-stage product of complement activation. sTCC is part of the complement system and originates from the terminal pathway, which is initiated after activation of any of the three complement pathways: the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways. All pathways lead to a common point, the activation of complement protein C3. After initial activation, the formation of the C5-convertase is initiated. This convertase then activates C5 into C5b, which forms the starting point of the terminal pathway (TP). Similar to C3 family members, C5b undergoes a conformational change that allows it to associate with C6 and C7, initiating the formation of an irreversible complex (C5b-7). This complex associates with the membrane of a pathogen or host cell. C8 subsequently associates with the complex and undergoes a conformational change allowing the so called β-hairpins to extend long enough to insert through the bacterial membrane. Hereafter, multiple C9 molecules associate with the C5b-8 complex and begin pore formation. The C5b-9 is now a heteropolymeric complex that consist of the terminal proteins C5b, C6, C7, C8, and C9.
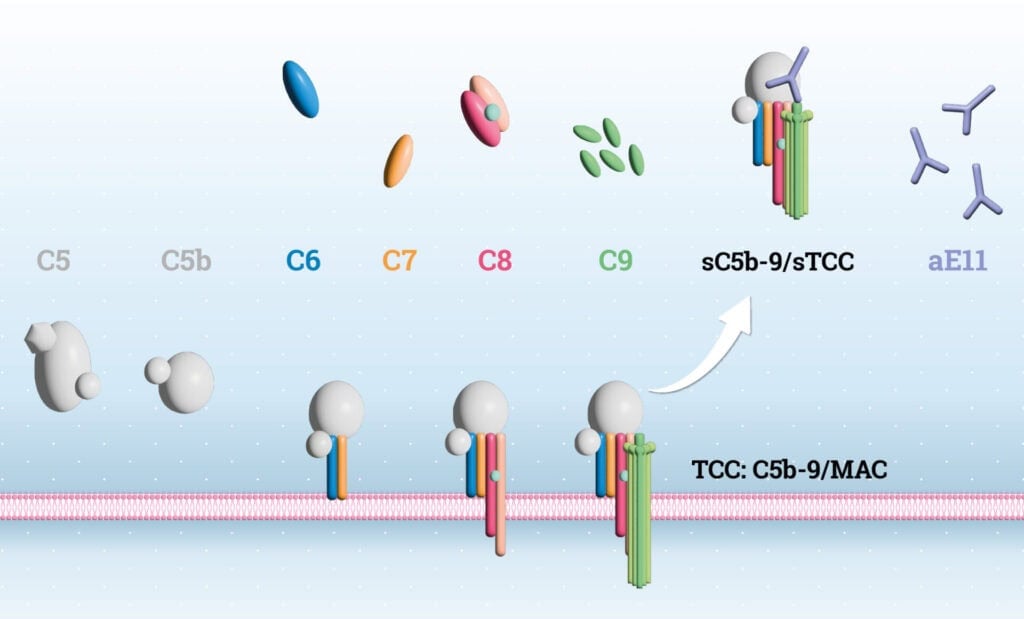
Figure 1: Schematic representation of complement activation and the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) and its soluble counterpart (sC5b-9/sTCC). Upon complement activation, C5 is cleaved to generate C5b, which initiates the sequential, non-covalent binding of complement components C6 through C9, resulting in the assembly of the pore- forming MAC on pathogen surfaces. Concurrently, C5b can also associate with C6-C9 in the fluid phase, forming soluble intermediates that lead to the generation of sC5b-9/sTCC. These soluble complexes bind to regulatory proteins such as vitronectin and/or clusterin, preventing their insertion into host or microbial membranes. The presence of sTCC in plasma is the result of inefficient incorporation of the complex into cell membranes. TCC that is actually incorporated into cell membranes is not found in plasma, because it remains in the cell or particle fraction after centrifugation. The monoclonal antibody aE11 recognizes a neoepitope on C9 that is present in both membrane-bound MAC and the fluid-phase sC5b-9 complexes; however, the TCC ELISA (HK328) of Hycult Biotech specifically detects the soluble C5b-9.
C5b-9 has been characterized primarily as a cytolytic effector in which the effectiveness of MAC pores depends on both the number and size of C5b-9 channels. The pore length and charge distribution influence membrane insertion and therefore the outcome of cell survival. Charge properties, particularly the balance between hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions, modulate membrane interaction and stability. Exposure of hydrophobic sites on complement components (predominantly C5 and C9), enhances their affinity for the lipid bilayer, supporting stable insertion and membrane perforation. However, pore assembly can be inefficient, occasionally resulting in the release of a soluble, non-lytic form of sTCC. sTCC does not have a cellular receptor or distinct function and is widely regarded as biologically inert. Its levels reflect levels of the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) formation. The sC5b-9 complex or sTCC represents the degree of complement activation as well as the failure rate of the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) assembly, but does not integrate into membranes or induce direct lysis.
Given its role as a marker of complement activation, accurate and reliable measurement of sTCC is beneficial for understanding its impact on disease and immune regulation.
The essential of reliable sTCC measurement
Soluble TCC is a valuable marker for monitoring complement activation and immune-related diseases. The membrane attack complex is also important, because it causes a variety of non-lethal effects in nucleated cells, including stimulation of release of inflammatory mediators, and cell proliferation. As the soluble counterpart of MAC, sTCC levels reflect systemic complement activity and can therefore indicate dysregulated complement activation. Such dysregulated complement activation is linked to chronic inflammation and tissue damage in various conditions, including renal diseases such as atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) and neurodegenerative disorders like multiple sclerosis (MS) and Alzheimer’s disease. It contributes to excessive inflammation, endothelial damage, and neuronal degeneration. These findings highlight the need for precise monitoring of complement activation markers, positioning sTCC as a potential marker for disease progression and therapeutic approach.
On the other hand, the presence of sTCC in circulation does not necessarily result in direct cell lysis. This can occur, for example, in situations where sublytic or dysregulated complement activation contributes to disease processes without causing evident cytolysis, such as in autoimmune or inflammatory conditions. In these cases, the ability to accurately quantify sTCC, as the soluble counterpart of MAC, is essential for understanding the role of the complement system as well as for the targeted investigation of therapeutic approaches. To support research, Hycult offers a broad range of products suited for measuring sTCC.
Significance of sTCC/MAC in disease and diagnosis
Studies show changes in sTCC levels during infection, auto-immune disease and trauma. To measure sTCC accurately, immunoassays should make use of monoclonal antibodies that are highly specific. These antibodies should detect a neo-epitope, which is exclusively present on activation products. Thereby, preventing the detection of single, non-activated, complement proteins like C9, which we give a misleading result. Antibody aE11 (HM2167) is a neo-epitope antibody that specifically detects only complement component C9 bound to the sTCC/MAC complex. This antibody has been incorporated in several of our sTCC/sC5b-9 and pathway ELISAs (e.g. HK328, HK3010/12). The measurement of sTCC has not been translated into common clinical use. However, with the new complement inhibitors making their way to the clinic in the coming years, it may be beneficial to use sTCC as a biomarker or companion diagnostics. This to monitor therapy and adapt dosing. For example, studies have shown that sTCC levels correlate well with Eculizumab dosing. This highlights its potential as a biomarker for monitoring complement activation and inhibition.
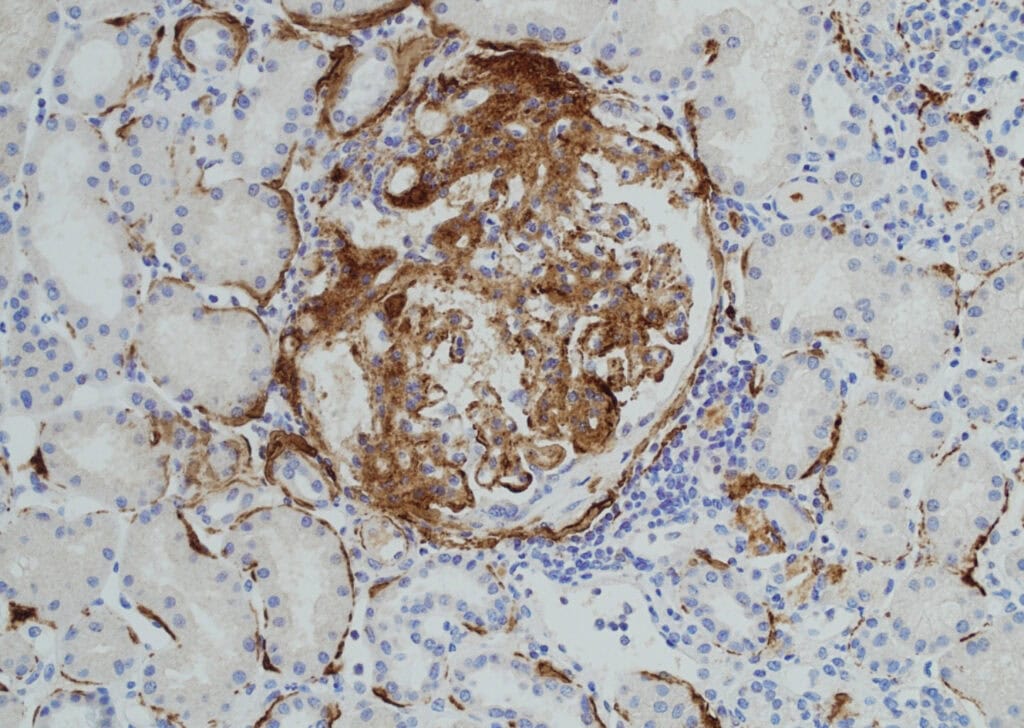
Hycult biotech offers also an anti-C5b-9 antibody for immunohistochemistry (IHC). In Figure 2 a staining of C3 glomerulopathy in kidney tissue is visible. The image was kindly provided by Prof. Lubka Roumenina. Prof. Lubka Roumenina, Professor at Centre de Recherche des Cordeliers, INSERM in France. As described in the FAQ section TCC/C5b-9 plays an important role in kidney-related diseases like C3 glomerulopathy. Antibody HM2443 anti-C5b-9 can provide information about the degree of tissue damage.
Inhibiting the Membrane Attack Complex assembly through factors like CD59, DAF, and MCP, offers therapeutic potential. However, dysfunction or deficiencies in these regulators can lead to uncontrolled activation and disease pathogenesis. As a result, understanding and measuring sTCC levels could provide insights into disease progression and the effectiveness of complement-targeted therapies.
Frequently asked questions
The membrane attack complex is formed during the terminal pathway of the complement system. First, C5 is cleaved by C5 convertase in fragments C5a and C5b. Hereafter, C5b rapidly binds C6 which is stabilizing the complex. This complex is subsequently recruiting complement component C7 and thereby enabling cell membrane insertion. Complement component C8 binds to the MAC precursor C5b6,7, which further anchors the complex and initiates small pore formation. Followed by multiple polymerizing C9 molecules that form a large β barrel transmembrane pore, the membrane attack complex. This transmembrane pore formation disrupts the osmotic balance, leading to cell lysis.
A distinctive feature of the MAC is its structural asymmetry, which influences both its assembly and function. During MAC formation, complement proteins undergo conformational changes that expose hydrophobic regions, allowing stable insertion into the target cell membrane. The presence of an asymmetric region provides mechanical stability and optimized pore formation. It interacts with surrounding membrane lipids and stabilizes the insertion process.
Charge distribution also plays a role in MAC assembly and function. The presence of a negatively charged patch on complement components such as C5b6 and C7 facilitates initial membrane association, helping to anchor the complex before full pore insertion. This electrostatic interaction between complement proteins and the target cell membrane ensures specificity as microbial lipids differ from host cells.
MAC is a flexible immune pore in which the amount of C9 molecules are variable, allowing adaptability in different membrane environments. This flexibility ensures that the MAC can effectively lyse the target cell. Moreover, the dynamic nature of MAC contributes to immune regulation, as sub-lytic concentrations of MAC components can trigger intracellular signaling events rather than direct lysis.
In conclusion, the build up of MAC from soluble complement proteins, and the interplay of structural elements such as asymmetry, and charge distribution ensures effective immune defence while minimizing unintended damage to host tissues.
sC5b-9 has multiple functions, it assembles on the surface of pathogens or dysregulated host cells and forms transmembrane pores that disrupt membrane integrity, which leads to osmotic lysis and cell death. Complement complex sC5b-9 also opsonizes cells in pathogen-infected tissues or organs, along with transformed or apoptotic cells, promoting their destruction. It also plays a role in pro-inflammatory signaling in which C5b-9 can activate intracellular signaling pathways leading to cytokine and chemokine release and inflammation (Sonia I. Vlaicu et al. 2019). Additionally, it could support anti-tumor immunity by targeting cancer cells. The formation of sC5b-9 on the surface of tumor cells can lead to direct lysis, or it may enhance opsonization by phagocytes and cytotoxic immune cells.
However, dysregulated or excessive sC5b-9 formation can contribute to pathology. For example, in patients with Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (aHUS) it can cause endothelial cell injury due to persistent C5b-9 formation. Among others, the membrane attack complex through kidney deposition is thought to play an important role in the pathogenesis of various kidney diseases by causing cellular injury and tissue inflammation, resulting in kidney dysfunction.
The difference between the Terminal Complement Complex (TCC) and the Soluble Terminal Complement Complex (sTCC) is that TCC is membrane-bound and cytolytic, whereas sTCC is soluble and non-cytolytic. Functionally, TCC can directly damage cells by inducing cell lysis, while sTCC serves as a biomarker of complement activation without causing cell lysis. TCC, also known as the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC), is formed on cell membranes. The composition of sTCC is similar to that of TCC, but is assembled in the fluid phase rather than on the cell membranes.
There is no difference between sTCC and sC5b-9. Both terms refer to the same complex, consisting of C5b, C6, C7, C8, and multiple C9 molecules. They are identical in composition and function, they just have different names.
- Kidney-Related Diseases (C3G, Lupus Nephritis, aHUS, MN): Characterized by complement dysregulation, immune complex formation, and inflammation, leading to glomerular damage, renal dysfunction, and progressive kidney disease.
- Hematological Disorders (PNH, AIHA, TMA): Conditions involving red blood cell destruction, thrombotic complications, and hemolytic anemia due to impaired complement regulation and immune system dysfunction.
- Neurological Diseases (Multiple Sclerosis, Alzheimer’s Disease, NMOSD, MMN, ALS, Parkinson’s Disease): Chronic neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders where complement activation contributes to neuronal damage, demyelination, and disease progression.
- Sepsis, SIRS & Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (IRI): Dysregulated immune activation leading to systemic inflammation, organ dysfunction, and tissue ischemia, relevant in conditions such as stroke, myocardial infarction, and trauma.
- Systemic Autoimmune Disorders (SLE, TMA-related conditions): Autoantibody formation and complement activation drive widespread inflammation, immune complex deposition, and increased disease severity.
- Oncology & Tumor Progression: Complement activation plays a role in the tumor microenvironment, influencing immune evasion, chronic inflammation, and cancer progression. Complement inhibitors are being explored as potential therapeutic strategies in oncology.
sTCC is a marker for terminal complement pathway activation. Membrane Attack Complex (MAC) formation indicates a degree of complement activation that can lead to cell lysis, making it a valuable tool for understanding of e.g. neuroinflammation, autoimmune diseases, and infection. Hycult Biotech provides a specific, high-sensitive and reproducible sTCC/sC5b-9 assay. This enables precise detection and quantification in among others, plasma and serum, but also in urine samples, when kidney integrity is compromised.
Advantages:
- 7-Point Curve – Offers precise quantification and flexibility in assay setup. Fulfills FDA and EMA guidelines.
- Superior Consistency – Ensures reproducible results across multiple experiments.
- Large Dynamic Range – Quantifies both low and high concentrations without additional dilutions.
- Multiple matrix Compatibility – Validated for use in plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, joint fluid and cell culture supernatant samples.
- Cross-Reactivity with NHP (non human primates) Samples – Ensures broader applicability for preclinical studies.
- Expert Support – Access to Hycult Biotech’s technical team for troubleshooting and protocol optimization.
- Another available species is Rat TCC Assay – Cat.# HK106
Contact us for more information
At Hycult Biotech, we recognize the growing demand for advanced complement research tools that facilitate accurate analysis and targeted intervention in immune-related diseases. Our portfolio includes high-quality complement pathway inhibitors (how to inactivate complement), complement assay kits, and monoclonal antibodies designed to support drug discovery and translational research. On our website, you can search for products that match your research needs. Additionally, we are happy to provide expert advice. Feel free to contact us via the contact form.