VCAM-1, Mouse, mAb 6C7.1
€133.00 – €320.00
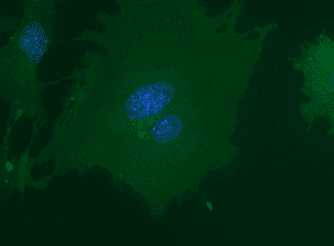
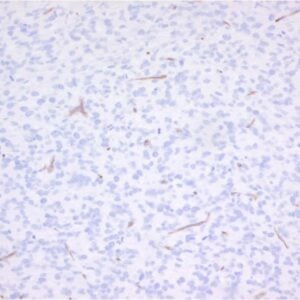
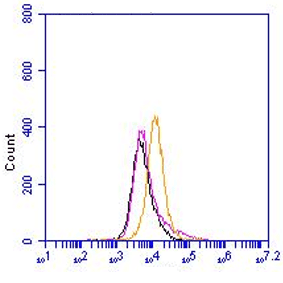
The monoclonal antibody 6C7.1 recognizes mouse vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1) (~ 81 kDa), a member of a subclass of the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF). IgSF members are ligands for integrins. Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) have important roles in the immune response, immune surveillance and cell-cell recognition, especially in leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. CAMs on the surface of leukocytes and endothelial cells are actively involved in the recruitment of specific leukocyte subsets into different tissues. VCAM-1 is expressed on inflamed vascular endothelium, as well as on macrophage-like and dendritic cell types in both normal and inflamed tissue. Cell adhesion molecules, like VCAM-1, are upregulated on cerebral vessels during inflammatory conditions of the central nervous system such as experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a model system for multiple sclerosis. Administration of monoclonal antibody 6C7.1 has been shown to inhibit or diminish clinical or pathological signs of EAE. VCAM-1 is a receptor for encephalomyocarditis virus on murine vascular endothelial cells. Expression of VCAM-1 on vascular endothelial cells is induced by TNF-alpha, IL-1, IFN-gamma or endotoxin. VCAM-1 is a ligand for the integrins alpha4beta1 (VLA-4) and alpha4beta7 (LPAM-1). These integrins are constitutively expressed by thymocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes. VCAM-1/VLA-4 interaction may play a pathophysiological role in immune responses and as well as in leukocyte emigration to sites of inflammation.